Automotive air conditioning is a vital feature in a car. Its primary task is to cool and remove humidity from the air. So, how does car ac work? This article discloses that for you.
Here is How a Car AC Work
A car air conditioning system works like a home or office AC system. It is crucial, more so during the warm weather.
In the modern world, it is difficult to find a current car without an AC system. The system gives you a comfortable and relaxed ride, especially during the summer season.
Some individuals do not know how a car’s air conditioning system works. Some assume that it is cold air in the vehicle.
But that is not true; the system has no capability of creating cold air. Instead, it removes the heat and moisture that already is in your vehicle.
This process leaves your car in a relaxed state, enabling you to enjoy your drive.
The AC system works by regulating the airflow in the car for an accurate temperature. Also, it ensures that there is no humid content.
As a result, the system enables you to cool and heat your vehicle’s interior better. Besides, it defrosts the windshield as well, thus giving you a clear view.
Understanding various air conditioning system components is crucial. It will help you understand how the process works better. Also, you need to know how they work.
How Air Conditioning System Components Work
With global warming, the weather has changed in the recent past. Most parts of the world have experienced hot and cold seasons. As a result, an air conditioning system in a vehicle becomes essential.
With global warming, the weather has changed in the recent past. Most parts of the world have experienced very hot and cold seasons. Consequently, an air conditioning system in a vehicle becomes essential.
As a result, vehicle manufactures came up with a car air conditioning system. It helps in cooling and warming the car.
The refrigerant gas is the most useful product in this system. It refers to a gas used to pressurize the air conditioning system.
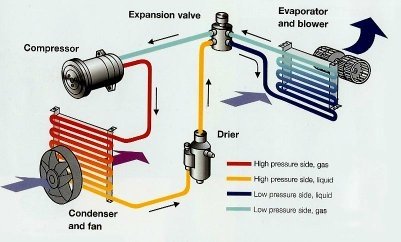
All a/c systems use similar components for the system to work. They are the compressor, receiver-drier, condenser thermal expansion valve, and evaporator.
Find more details about each component discussed below.
1. Refrigerant

Although it is not a component in the car air conditioning system, it is the system’s lifeline. It is not possible to meet a cooling comfort in your vehicle without the refrigerant.
While at low temperatures and pressure, it takes a gaseous form. Also, it takes a liquid form when subjected to high pressures and temperatures.
So, this gas is essential and plays a significant role in the a/c system. Every vehicle has a specified amount of refrigerant used in filling the order.
In passenger vehicles, it is usually about three or four pounds of a refrigerant at most.
2. The compressor
The compressor is a vital part of the car air conditioning system. It is a pump attached to the car’s engine crankshaft, which drives it by giving it power.
Its primary function, as the name suggests, is to compress the refrigerant. The refrigerant enters the compressor in a gaseous state and under low pressure.
When you turn your AC on, you compress the vaporized or gaseous refrigerant in this component. The aim of squeezing is to ensure it is under high pressure.
Driving the pump forces the gas out to the condenser. The compressors can only compress gasses and not liquids.
3. The condenser
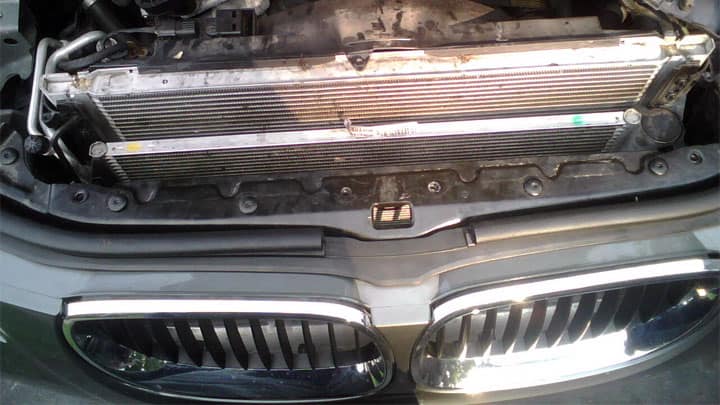

The main task of a capacitor in this system is to condense the refrigerant from the compressor. Condensation occurs as a result of rapid warm or hot air cooling.
The moisture or water vapor in hot air forms a liquid state after condensing.
In the modern automotive air conditioning system, this is the most recognizable part.
At this point, you turn the refrigerant from the gaseous state to liquid form. You achieve this condensation by pressuring the refrigerant.
The condenser cools down the refrigerant by the air that flows around the tubes. The cooling down process turns the gas into a liquid.
So, the refrigerant turns into a high-pressure fluid. At this point, it is ready to enter into the next component.
4. Receiver-Dryer
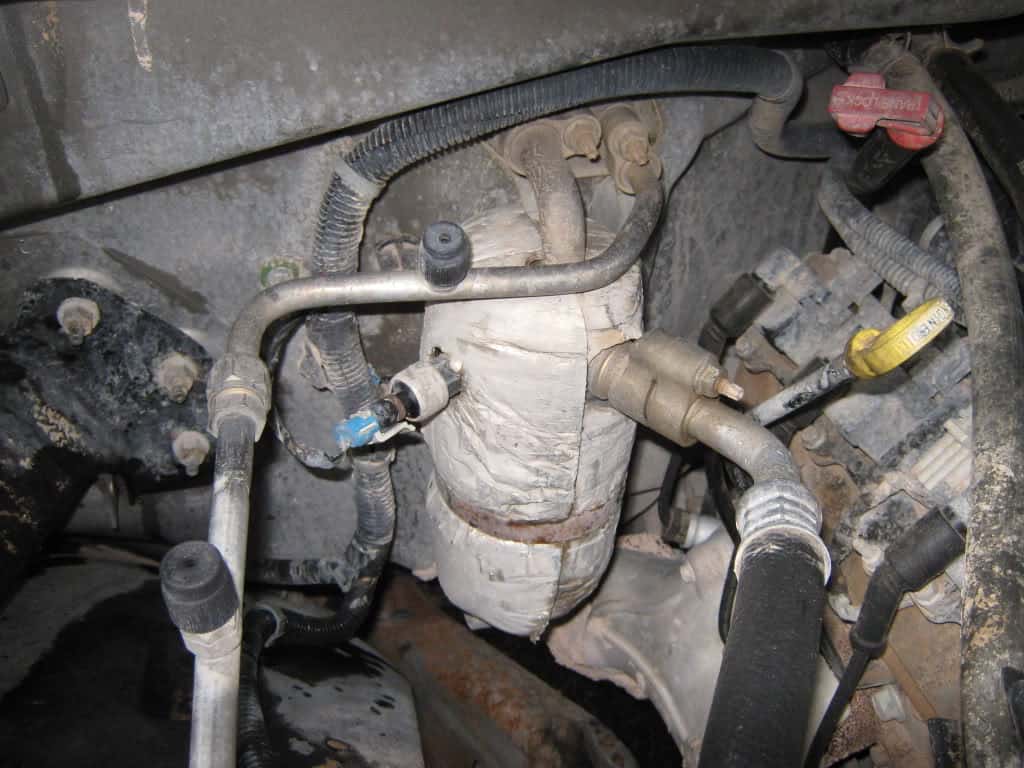

This component acts as a reservoir. It prepares the liquid for a transfer to the evaporator. Yet, in this reservoir, there are desiccants, which is a drying agent. Desiccants are small granules that attract water.
The removal of the water element at this stage is essential. Failure to remove it at this point, it may turn into ice crystals.
These ice crystals are capable of harming the entire air conditioning system. The desiccants in this stage remove all water elements, thus safeguarding the system as a whole.
Collapsing of the a/c system in your vehicle can make your driving uncomfortable. Although you can open your windows during the hot season, it is not very useful.
Windows may bring in the excess wind as you fast drive, thus making you uncomfortable. Also, it might let in unwanted substances such as dust.
5. Thermal Expansion Valve
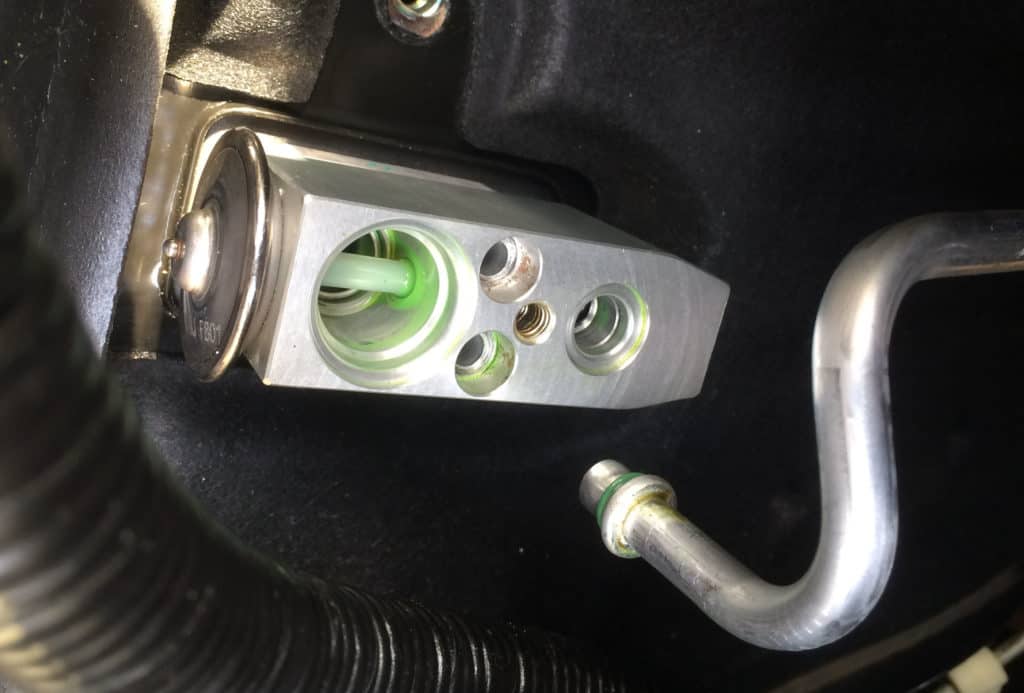

In this valve, liquid expansion occurs by changing the high-pressure into low-pressure. The expansion minimizes pressure on the refrigerant.
As such, it prepares the fluid further before transferring it into the evaporator.
The valve’s design helps it to sense pressure and regulate the refrigerant flow. It also allows for the steady operation of the system.
The valve’s moving parts may sometimes wear out, thus requiring replacement.
Also, instead of using the valve in question, you can use an orifice tube. Still, it performs the same task, which is allowing refrigerant expansion.
It reduces the force as well, before the refrigerant gets into the next component.
Besides, the orifice tube does not have moving parts. It allows the refrigerant flow at a constant speed.
But, over time, it gets clogged with debris. A system that uses an orifice tube turns the system off and on. It does this to control the refrigerant flow.
6. The Evaporator

The evaporator is the central part of the air conditioning system. Its location is the cabin, on the passenger’s side.
All the other AC components are in the engine compartment. The evaporator has a similar design with a radiator.
But it is smaller in size and has tubes and fins. The design of these tubes and fins helps in heat absorption.
As refrigerant gets into the evaporator coil, it freezes at zero degrees Celsius. The low temperatures are the reason why you need to remove all the water. Also, the refrigerant gets into the evaporator coil in low-pressure fluid form.
However, this refrigerant does not freeze at zero degrees. But its boiling point is relatively low.The car cabin warmth is enough to ensure R -134a in this component boils.
After boiling, the R-134a changes into a gaseous state, which assists it in heat absorption.
For the vehicles that use the orifice tube system, it works differently. The system has an accumulator located between the compressor and the evaporator.
Sometimes, this tube releases excess refrigerant to the evaporator.
The compressor can only compress gas and not liquid. Thus, the accumulator attracts excess fluid before entering the compressor.
Also, the evaporator absorbs humidity in the vehicle, hence making you feel fresh.
Dirt, moisture, and pollen condense on the evaporator’s coil. If some water starts dripping underneath your car after stopping, it’s the AC evaporator.
Such dripping should not worry you, and your vehicle is in good condition.
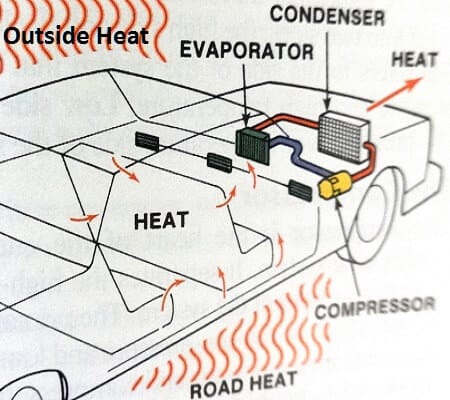
The Process of Cooling Air in an AC System
This process starts at the vehicle’s air conditioning compressor. It is where the refrigerant compression into the high-pressure state occurs.
The compression causes the refrigerant to liquefy. It then travels to the condenser, through high-pressure lines.
The condenser lets the liquid mix with the outside air. The mixing makes the atmosphere absorb heat from the liquid.
Then, the fluid flows either into the orifice tube or into the expansion valve. Here, it changes into a gaseous form in the air conditioning system’s low-pressure side.
It then flows into the accumulator containing a desiccant bag. The bag collects the unwanted moisture, among other impurities.
The clean refrigerant then flows into the evaporator through the tubing. In this state, it can collect heat from the air going through the fins. This process leaves behind the cooler air.
Conclusion
Finally, now you have understood “how does car AC work.” All the components work together by each contributing its part.
However, all the elements are essential. If one part fails, the entire process collapses. Thus, you must ensure that every piece is in good condition.
The car air conditioning system has three tasks to perform. First, cooling the car interior is very vital, especially during the hot season. It ensures that you have cold temperatures in your car.
Besides, heating the interiors during the cold seasons is also significant. You need warmth in your car when it’s cold outside.
Last of all, defrosting the windshield is the most crucial task for the AC system. It is usually frustrating when you keep on struggling to see through your windshield.
As a result, it can affect your driving, leading to an accident.








